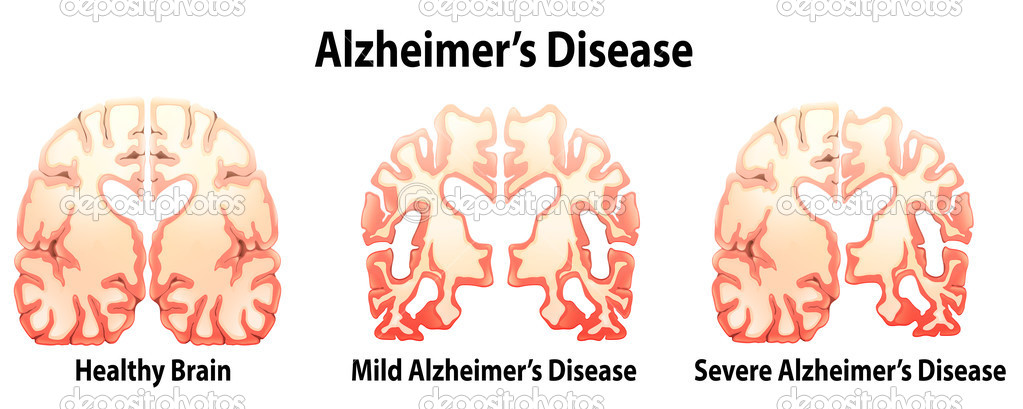
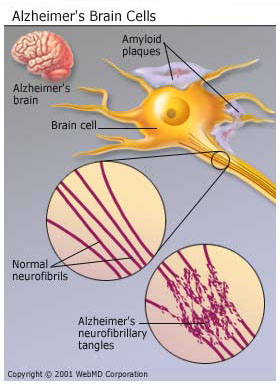
Alzheimer’s disease or AD is an incurable disease of the brain that steals people’s memory. It is caused by the deterioration and ultimate death of neurons (nerve cells) in a number of areas of the brain. Patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease lose mental functions such as the ability to learn new things and short-term memory at first and they lose control over their sense of their emotions, direction and other aspects of behavior in the later stages of AD. The end stage of AD is in the loss of control of body functions, inability to eat or shallow and finally death from infection or malnutrition. It is the most common cause of dementia (loss of cognitive abilities) in the elder age.
A German psychiatrist and neuroanatomist named Alois Alzheimer identified Alzheimer’s disease in 1906. This disease is now considered a very serious threat to public health because the number of people suffering from this disease is increasing rapidly which increases the direct and indirect costs to the people suffering from it.
TYPES OF ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE:
- Early – Onset AD
- Late – Onset AD
- Familial Alzheimer’s Disease (FAD)
CAUSES OF ALZHEIMER DISEASE:
- Family history of AD
- Having Down syndrome
- History of head injury
- Immune system problems
- Certain genes
- Unusual protein deposits in the brain
- Most of the experts are of the view that Alzheimer’s disease is not a normal part of aging.
- A study reveals that 72 percent or three out of four Alzheimer’s patients had gone through harsh emotional stress during the two years earlier their diagnosis. These incidents might include:
- Judgment of a family member’s severe illness
- Financial problems
- Car accidents
- Violent experiences like robbery or attack
- Sadness, death of life partner, child or close friend or relative.
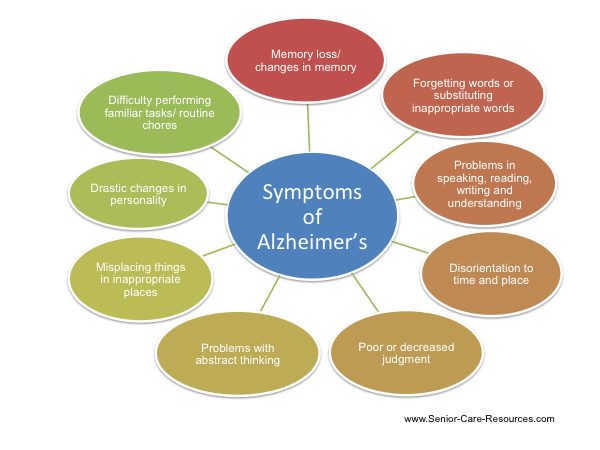
KEY SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE:
KEY SIGNS OF NORMAL CHANGE V/S. EARLY ALZHEIMER’S SYMPTOMS:
| Normal | Early Alzheimer’s Disease |
|---|---|
| Feel sad intermittently | Occurrence of fast mood swings, from tears to rage, for no visible reason |
| Making an occasional wrong turn | Get lost in familiar places and don’t know how to go home |
| Annul a meeting date with friends | • Sleep far more than usual • Sit in front of the TV for several hours • No interest in usual interests and activities |
| Forget to record a verify | Unable to maintain checkbook, balance figures, solve problems, or consider theoretically |
| Can’t come across a recipe | Can’t pursue recipe directions |
| Experience the cold more | Wear Dress not considering the weather |
| Forget conversation details immediately | Forget the whole conversations regularly |
| Look for informal names and words | Forget the names of family members and common objects and substitute words with unsuitable ones |
RISK FACTORS OF ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE:
- Age: Increasing age is the greatest known risk factor for Alzheimer’s because the risk of this disease increases immensely when you reach age 65. Also, the folks with rare genetic changes start experiencing Alzheimer’s symptoms as early as their 30s.
- Family history and genetics: The risk of developing Alzheimer’s becomes double if your parent or sibling has the disease.
- Sex: Women live longer and are more prone to develop Alzheimer’s disease than men.
- Mild cognitive impairment: People with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) might have memory problems and might have an increased risk of developing dementia.
- Past head trauma: The people who have a harsh head trauma or repeated head trauma- have a greater risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
- Lifestyle and heart health: There is no certain lifestyle factor that conclusively show the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. But, following some factors put you at risk of heart disease and increase the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease:
- Lack of fruits and vegetables in diet
- Poorly controlled diabetes
- High homocysteine levels
- High blood cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
SOME TIPS TO AVOID ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE AND MAINTAIN HEALTHY BRAIN FUNCTION:
- Avoid fructose and sugar – Try to keep your sugar levels at a minimum level and focus that your total fructose below 25 grams per day or as low as 15 grams a day if have insulin resistance or any related disorders.
- Avoid casein and gluten – Research shows clearly that your blood-brain barrier is negatively affected by gluten. Gluten makes your gut more leaky, which allows proteins to store in bloodstream. This sensitizes your immune system and promotes irritation and autoimmunity- both of which play a great role in the development of Alzheimer’s.
- Eat fermented foods or consume a high quality probiotic supplement to optimize your gut flora.
- Increase the consumption of healthful fats such as avocado, wild Alaskan salmon, free-range eggs, pecans and macadamia, organic virgin olive oil, coconut oil, olives, clarified butter, raw milk, etc.
- Reduce your overall calorie consumption significantly.
- Improve your level of magnesium.
- Increase your vitamin D levels with safe sun exposure.
- Keep your fasting insulin levels under 3.
- Eat a nutritious diet daily.
- Do away with mercury from your body.
- Avoid aluminum.
- Exercise regularly.
- Avoid flu vaccinations because they both mercury and aluminum, recognized neurotoxic and immunotoxic agents.
- Eat blueberries
- Avoid stress as far as possible
- Avoid anticholinergic and statin drugs.
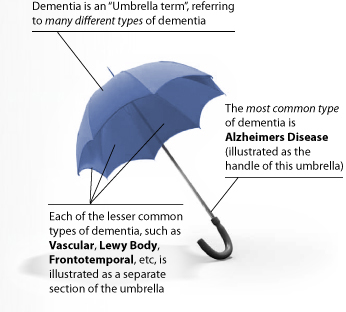
Dementia:
If you are over the age of 65 and you are becoming more and more forgetful, it might be the early signs of dementia. Memory loss becomes a problem when you get older as your memory is affected by medications, certain illnesses, tiredness, stress and increasing age.
Dementia is a common condition when you reach the age of 65. It is a syndrome of the declining brain and its abilities and problems such as memory loss, thinking speed, mental agility, understanding and Judgment.
SYMPTOMS OF DEMENTIA:
- Memory Loss Isn’t automatically Dementia
- Delicate Changes in Short-Term Memory
- Difficulty in discovery of the Right Words
- Changes in Mood
- Apathy
- Difficulty in Doing daily works
- Confusion
- Difficulty in subsequent Storylines
- A Failing wisdom of Direction
- Being monotonous
- Struggling to become accustomed to Change
CAUSES OF DEMENTIA:
- Mainly Dementia is caused by harm to brain cells.
- Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease or Pick’s Disease, Huntington’s Disease, Parkinson’s disease, head injury, brain tumors, simple and normal pressure hydrocephalus, infections (such as meningitis, HIV / AIDS, or syphilis), hormone disorders, metabolic disorders, hypoxia, nutritional deficiencies, drug abuse, or chronic alcoholism also cause Dementia.
DEMENTIA DIAGNOSIS
- Medical history
- Medication history
- Complete physical exam
- Laboratory tests
- Neurological exam
- Neuropsychological tests
DEMENTIA TREATMENT:
- Medications to treat Dementia:
- Improve the quality of life.
- Relieve the load on caregivers.
- Make late in admission to a nursing home.
- Dementia treatment with optional medication, natural supplements:
- Consume several natural supplements such as Mind Power Rx, ginkgo biloba and vitamin B complex to treat Dementia.
- Eat lot of fruits, vegetables and fish and get diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids which decrease the risk of developing dementia.
- Take Green tea as it decreases the risk of Dementia.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DEMENTIA AND ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE:
A number of people don’t know the differences between Alzheimer’s and dementia. Have a look at main differences written below:
- Dementia is not a disease itself, but it is a syndrome, or group of symptoms whereas Alzheimer’s disease is one type of dementia.
- Outcomes of Dementia and Alzheimer’s disease:
| Dementia | Alzheimer's |
|---|---|
| A lot of causes of dementia are reversible such as thyroid imbalances, infections, malnutrition, medication interactions, vitamin B12 deficiency and depression. A few Medicines for common conditions such as diabetes, arthritis, insomnia, high blood pressure, depression create side effects that imitate dementia. A number of conditions lead to irreversible dementia. | The progressive brain damage and dementia caused by Alzheimer's disease is unalterable. Treatments are available to decrease the rate of decline caused by Alzheimer's, but no cure available as yet. When the disease reaches to its final stage, the brain suffers extensive damage and shrinkage and results in death of the patient. |