A biopsy is a kind of diagnosis process in which a very small amount of tissue or cells from the body are removed for the sampling purpose. After that, it has undergone through laboratory test where it is analyzed whether the sample taken is cancerous or non-cancerous. There are different types of biopsy depending upon the area of the body which is needed to be diagnosed.
The importance of biopsy test in medical science is enormous as it ensures a patient would not mistreat under any situation by analyzing the detail cause and type of disease.
This test is generally recommended by the doctors in the cases where other diagnostic procedures itself cannot determine a condition and needs close and thorough analysis to come into a conclusion for a disease to start with a right form of treatment.
If anyone develops any suspicious symptoms that a doctor thinks needs biopsy will be a final diagnostic test for determining the situation then they will ask for the same. Mostly biopsy is required in cases of unusual growth in body or suspicious conditions in the body that a doctor suspect as cancerous.
However other than cancer, a biopsy can be required for diagnosing other health conditions too where any imaging test shows a suspicious growth or condition. Depending upon the area of biopsy either biopsy will be done alone or it will be coordinated with other diagnostic methods like CT scan, MRI, etc.
An abnormal tissue which is taken for the biopsy is called as a tumor, lesion or a mass. Theses suspicious bodies are either noticed through the imaging test or during the physicals examinations (like lumps in breast).
Once the sample cells or tissues are collected then it is sent in the laboratory for closer examination. In the majority of the cases of cancer, the treatment starts only after the biopsy test. However in other health conditions too this test is required to begin with the appropriate treatment.
Biopsy Types
Table of Contents
There are various types of biopsies and almost in all of them, a sharp tool is used for removing the tissue samples. Depending upon the area of biopsy local anesthesia or numbing medications are given to the concerned patient so that they won’t have to suffer from pain during the procedure.
Needle Biopsy
In this type of biopsy, a special needle is used by the doctors for removing the tissue sample from the suspicious location of the body. The needle biopsy is mostly used in cases where an abnormal growth is identified during the physical examination test.
For example in the cases of breast lumps, it can be felt through skin touch, more abnormal than the surrounding skin areas. However, a needle biopsy is also used in cases where an abnormality cannot be felt through the skin. In such cases, it is combined with other imaging procedures to complete the biopsy process. Local anesthesia is given to the patient for minimizing the pain severity during the biopsy procedure.
Needle biopsy sub-types include the following:
Core Needle Biopsy
In the core needle biopsy, a large needle with cutting edge is used to remove a column of tissues from the suspicious location.
Fine Needle Biopsy
In the fine needle biopsy or aspiration, a long thin needle is inserted in the suspicious area where from a sample of fluid or tissues are taken through a syringe.
Image-Guided Biopsy
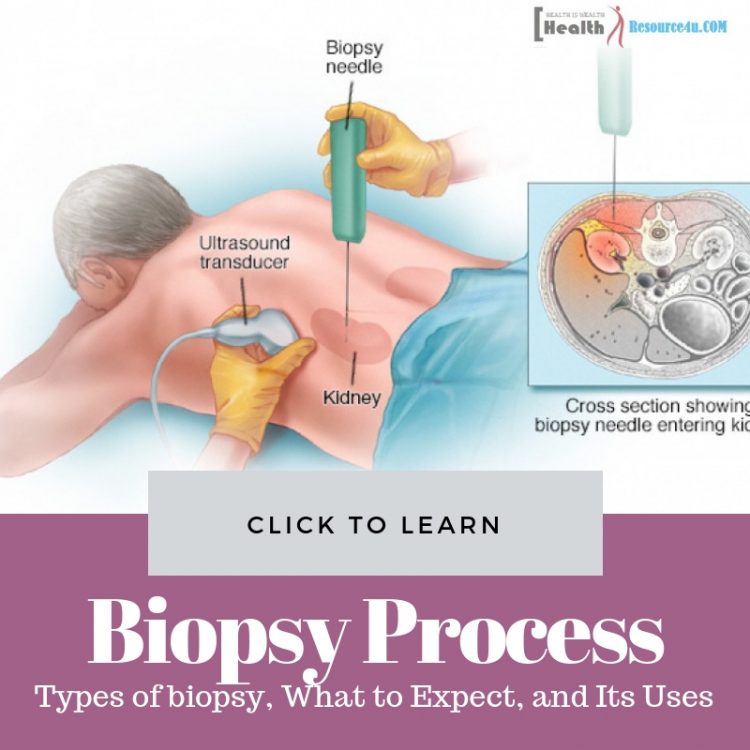
In the image-guided biopsy, the process is completed with the help of other imaging tests such as X-ray, CT and MRI or ultrasound along with the needle biopsy. During the process the said imaging procedures guide a doctor to reach the suspected area which cannot be felt through the skin.
Cases, where image-guided biopsy is required, include abnormal growth in lung, liver, and prostate. These images ensure that a needle reaches the correct location without any issue.
Vacuum Assisted Biopsy
In the vacuum-assisted biopsy, a suction device is used to increase the number of tissues or fluids which are removed or drawn through a needle. This minimizes the necessity of several insertions of a needle for collecting the needed amount of cells or fluid samples.
Endoscopic Biopsy
In the endoscopic biopsy process, a flexible, thin tube (endoscope) is used which has a light in its end to check the internal structures in the body clearly. A special tool is passed through the endoscope to draw the sample tissue for analyzing it in the laboratory.
Depending upon the location of the suspicious area the type of endoscopic biopsy depends. Also as per the type of endoscopic biopsy, a patient will be given sedative or anesthetic before the biopsy process starts.
The tube which is used in endoscopic biopsy is inserted in the body via rectum, urinary tract, mouth or through a small incision in the skin. The endoscopic biopsy which is used for collecting tissue from the bladder is called Cystoscopy, tissue removal from the lung is called Bronchoscopy and tissues which are collected from the colon are called Colonoscopy.
Skin Biopsy
During the skin biopsy tissues or cells are collected from the body surface. In the suspicious skin condition such as melanoma and other such cancers, skin biopsy are required. Skin biopsy procedures have different type and the type of skin biopsy you will undergo depends upon the type of cancer suspected by the doctor and its growth extent. A patient is given a local anesthetic to numb the biopsy area before the procedure starts.
Punch Biopsy
In the punch biopsy, a circular tool is used to remove cells from the deeper layers of your skin.
Shave Biopsy
In the shave biopsy, a doctor uses a tool similar to a razor for scrapping sample from your skin surface.
Excisional Biopsy
In the excisional biopsy, a doctor removes the whole lump or full abnormal areas of skin. The concerned patient is given stitches to close the treated area.
Incisional Biopsy
In the incisional biopsy process, a scalpel is used for removing a small area of the skin. In this type of skin biopsy, you may or may not receive stitches that depend upon the area of skin which is removed.
Bone Marrow Biopsy
Under the condition where an abnormality is detected in blood or if your doctor suspects any cancerous growth that is originated or traveled to the bone marrow, in those cases bone marrow biopsy is required.
Bone marrow biopsy is conducted to diagnose a different variety of blood issues which includes both cancerous and non-cancerous. Certain cases where bone marrow biopsy is required includes blood cancer such as multiple myeloma, lymphoma, and leukemia.
This biopsy test also helps to diagnose cancers which are originated in other places but have traveled to bone marrow. Bone marrow is a spongy material that is found in some of the larger bones in the body where the blood cells are produced. This biopsy test determines the reasons which are causing abnormalities in the blood.
Generally, in the bone marrow biopsy, a bone marrow sample is taken from the back portion of hipbone through a long needle. However, bone marrow biopsy can be done from any other areas of bone too. A local anesthetic is given to the patient to minimize the pain before starting the biopsy process.
Surgical Biopsy
Under the cases where the suspected cells or area cannot be reached through any other biopsy procedure then in those cases, a surgical biopsy is the ultimate option. This biopsy test also helps to come into a conclusive decision where all other biopsy tests are failed in giving any particular conclusion.
In this type of biopsy, an incision is done by the surgeon in the patient’s skin to reach the suspicious location or cells. The surgical biopsy can be used to remove a certain part of the abnormal cells i.e. incision biopsy.
Also, a surgical biopsy can be done to remove the entire areas of the abnormal cells or tissues known as an excisional biopsy. Some common cases where surgical biopsy is utilized include surgery for removing lymph node for diagnosing lymphoma, surgery for removing breast lump for diagnosing breast cancer, etc.
In some cases of surgical biopsy general anesthetics are given to the patient for keeping the patient unconscious throughout the surgery process. Whereas in some cases of surgical biopsy a patient is given a local anesthetic to numb the location of the biopsy.
As per the biopsy invasiveness, a patient may be required to stay in the hospital for a few days or for a few hours after surgery for the follow-up or observation.
Laparotomy and Thoracotomy
Laparotomy is a surgery in which cuts are done into the abdomen or belly from upper to lower abdomen also known as a vertical cut. It is done in cases where a suspicious location can’t be diagnosed through other tests such as laparoscopy or needle biopsy.
In this process, a sample tissue is drawn from a suspicious location. This procedure helps to detect the actual affected area and its growth extent. Also, nearby tissues are detected to determine whether they are healthy or developing cancer.
In this surgery procedure, general anesthesia is given to the patient to make them sleep throughout the procedure so that he or she will not feel the discomfort that develops during the process. In the surgery process where the chest is opened instead of the abdomen area is known as Thoracotomy.
Laparoscopic and Thoracoscopic
A laparoscopic biopsy is quite similar to the endoscopy but in this process scope that is used is slightly different than the scope used in the endoscopy. In this procedure, a laparoscope is used to look inside the belly or abdomen and a sample tissue is removed from there.
In this process, a very small cut is done in the abdomen and then the laparoscope is passed through the cut into the abdomen to look the internal area. Similar procedures which help to look into the chest are called as Thoracoscopic and Mediastinoscopic biopsy.
What to Expect from the Biopsy Process
The biopsy is an effective diagnostic procedure that helps to determine the actual causes of any suspicious growth in the body where all other tests cannot give any conclusive result.
The biopsy process will vary depending upon the difficulty that includes for removing the suspicious tissue from any particular area. The more difficult the processes are called invasive and less difficult processes are called minimally invasive biopsy.
The minimally invasive biopsy can be done on the same visit day at the doctor’s clinic. In this type of biopsy, numbing medication is given through injection which doesn’t let the patient feeling any pain at all. Most of the skin biopsies come in the category of a minimally invasive biopsy.
In the cases of invasive forms of biopsies, a patient requires to be hospitalized for the processing. For this, a pre-appointment is required to be taken to conduct the process on the pre-decided date.
In these types of biopsy process sedating are given to the patient before the beginning of the process to ease the discomfort during the procedure. After receiving the sedating and pain killer medication you will remain still and won’t feel any pain throughout the process.
After the biopsy, a patient may feel soreness around the biopsy area for the next few days. However, it will automatically disappear after some time. A doctor may prescribe a pain relief medication to relieve the little pain and discomfort that lasts after the biopsy process.
Mostly biopsy is considered as an outpatient process as because a patient can go home immediately after the processing. The preparation process of biopsy that a patient requires to adhere depends on the type of biopsy which is about to be processed.
For minimally invasive biopsies such as fine needle biopsy, there is no preparation is required as it is done on the same visit at the doctor’s clinic.
In the cases of more invasive biopsies, consent is required to be signed which denotes the agreeing from the patient side for the processing. A patient wears a gown during the procedure instead of their personal clothes.
In some cases of biopsy, a patient requires not to eat anything from before the few hours of the actual processing time. The type of anesthesia given during the procedure depends on the invasiveness of the process.
In the biopsy process where tissue is required to be removed from an internal organ, general anesthesia is given to the patient and patient need to stay in hospital at least for one day.
In less invasive biopsies local anesthesia is given to numb the location which is going to be processed. In these cases, a pain relief medication may or may not be given to the patient by the doctors.
In certain types of biopsies where an incision is done, stitches are given and dressing is done. Under the cases of biopsy where sample tissues are taken from cervix or womb lining, light bleeding from the vagina may occur.
Uses
A biopsy is mostly conducted to diagnose cancer but other health conditions too may require biopsy for diagnosing the actual cause of disease, its progression rate, and location. Under the conditions where biopsy test is mostly used are mentioned below-
Cancer
If anyone develops any lump or swelling in any body parts without any definite or known reason then in those cases to determine whether the abnormal growth is cancerous or not, the biopsy will be a trustworthy procedure.
Peptic Ulcer
A biopsy can be required to diagnose the ulcer, whether it is caused by a Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs intake or not. In such cases, a small bowel biopsy is done to determine the anemia, mal-absorption and celiac disease.
Diagnosis for Kidney Disease
A kidney biopsy is required in the cases of kidney failure to determine the extent of damages in the kidney, any suspicious tumor in a kidney or an inflammation. It helps to diagnose the body’s rejection if it exists in the cases of a kidney transplant.
This type of biopsy is done with the help of imaging test which guides to reach the actual location for removing a tissue sample from the kidney.
Diagnosis for Liver Disease
Any suspicious abnormalities in the liver are diagnosed through the liver biopsy. This helps to determine a doctor whether the sample tissues taken from the liver are cancerous or not. In the cases of long term hepatitis, this biopsy helps to assess whether the treatment is working for the patient or not.
Also, it helps to diagnose liver fibrosis or cirrhosis where a liver is fully scarred due to long term alcohol consumption, any long term disease or any past injury.
Inflammation Detection
Biopsy test helps to determine the reasons which are particularly causing inflammation in the body. In the cases of organ, transplant biopsy helps to assess whether the body is rejecting the transplanted organ or not. Also, it determines whether the diseases which have caused the transplant necessity is developing again or not.
During the biopsy process if requires then at the same time a suspicious tumor or lump will be removed which also comes in the biopsy process.
Infection Detection
Biopsy test such as needle biopsy helps to diagnose the existence of any infection in the body. Also, it determines what organ is causing so.
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Detection
In the cases of uterus bleeding biopsy test such as endometrial is done in which uterus lining is taken as a sample to examine whether the uterine bleeding is caused by cancer growth or due to some other reasons.
Diagnosis for Male Infertility
Biopsy test also helps to diagnose male infertility. For example, testicular biopsy is done to determine the actual cause of infertility in male. This type of biopsy can be done via a needle or through a small cut in the skin or via surgery process.
Testicular biopsy is not preferred for diagnosis testicular cancer as it increases the risk of spreading if it exists. Instead, an ultrasound test is done for diagnosing testicular cancer.
Nerve Damaging Diagnosis
Biopsy test helps to diagnose any damages in small nerves, inflammatory nerves, destruction and degeneration in nerves, etc. The nerve biopsy is mostly done via the surgery process to ensure full safety.
In the end, we can conclude that all types of biopsy carry a special place and effectiveness on its own space for different organs. So each one of them is important that makes it a vital and effective diagnosis process to analyze and determine both cancerous and non-cancerous diseases and conditions.
[expand title=”View Article Sources“]
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cancer/in-depth/biopsy/art-20043922
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/174043.php
- https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=biopgen
- https://www.cancer.org/treatment/understanding-your-diagnosis/tests/testing-biopsy-and-cytology-specimens-for-cancer/biopsy-types.html
[/expand]