Diabetes: A Chronic Condition
Table of Contents
Photo By: AJC1/ CC BY
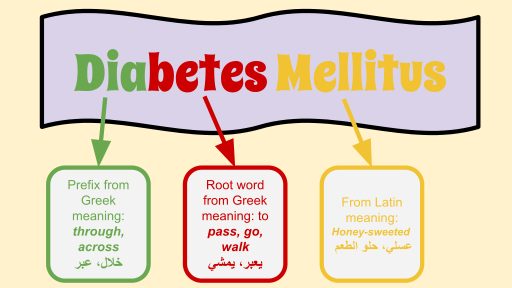
Diabetes (also known as diabetes mellitus) is a chronic medical condition that is lifelong. Though it has no known cure, symptoms can be managed. This disease affects the ability of the body to use energy found in foods. This is a major lifestyle disease and as its prevalence and incidence increase in modern times, the present research seeks to uncover the secrets behind this metabolic syndrome.
Kinds/Types of Diabetes
All the three different types of this disease have the same underlying problem namely regulation of blood glucose levels, Generally, the body breaks down sugars and carbs into a special body sugar called glucose. This provides fuel and energy for your body. Cells in the body also need insulin. This is a hormone found in the bloodstream which influences how blood glucose is utilized for boosting energy. Diabetes mellitus either involves the body making less insulin or inability to use the insulin or a blend of both. As the cells cannot take in glucose, in such a medical condition, this builds up in the bloodstream. Continuously high levels of underutilized blood sugar levels can damage the minute blood vessels found in different parts of the body:
- Eyes
- Kidneys
- Heart
- Nervous system
- In fact, a type of blindness called due to diabetes called diabetic retinopathy is also prevalent. Diabetes, if left untreated, can cause problems such as heart disease, stroke, blindness, kidney issues, and even nerve damage.
Type 1 Diabetes
This is also known as insulin-dependent diabetes. It also is called juvenile onset disease as it commences in childhood. This diabetes type is an autoimmune medical disorder. It is caused when the body attacks the pancreas with antibodies. In persons with type 1 diabetes, damaged pancreatic conditions lead to zero insulin production.
This is a disease type which may be caused due to genetic factors. It could also be the consequence of faulty beta cells in the pancreas that are responsible for insulin production. Numerous medical risks have been linked to this form of diabetes. Damage to tiny blood vessels in the eyes, nerves, and kidneys are known as diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy respectively are common conditions linked to type 1 diabetes. Heart diseases, as well as strokes, are also linked to this disorder.
Treatment for this type of diabetes involves the injection of insulin into the fatty tissue below through the skin. Methods of injecting insulin are as follows.
- Syringes
- Insulin pens
- Jet injections
- Insulin pumps
Insulin pens work using cartridges and a fine needle. Jet injectors make the use of pressure to send insulin sprays through the skin. Insulin pumps release insulin through flexible tubing to the catheter under the ab skin. Test A1C is carried out to check blood sugar levels and assess organ damage and other possible complications from diabetes.
From careful mean planning to regular exercise and monitoring of blood sugar levels as well as taking insulin and other required medications are some of the interventions for this type of diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes
Photo By: Sandra Cohen-Rose and Colin Rose/ CC BYThis is the most well-known form of the disease that occurs, with 95% of the cases occurring in adults of this kind only. This is known as adult onset diabetes. It has been observed in teenagers now, though. It was also referred to as non-insulin dependent type of diabetes.
This is considered a milder form as against type 1 diabetes, But it can still lead to a lot of health complications, especially in the smallest blood vessels of the body that supply nutrients to the eyes, nerves, and kidneys. This type of disease also raises the chances of heart disease and stroke.
In this type of diabetes, there is some production of insulin by the pancreas. But, either the amount produced is not enough to meet body needs or cells have a resistance to it. Insulin resistance takes place in the following types of cells:
- Adipocytes/fat cells
- Liver cells
- Muscle cells
Those who are obese with more than 20 percent of their ideal weight for their height can develop this type of diabetes. Obesity brings insulin resistance with it because pancreas has to work harder to produce enough insulin for the body. This is generally not enough to keep sugar levels normal.
Currently, there is no cure for this type of diabetes, which can, however, be controlled with weight management, exercise and a healthy diet. Diabetic medications are often needed as the course of this disease is generally progressive. An A1C blood test may be carried out to manage average glucose levels in the blood over the past 3 months,
Gestational Diabetes
This is diabetes triggered by pregnancy. It is characterized by insulin resistance and often occurs during the middle or later stages of pregnancy, As high blood sugar levels are circulated to the baby from the mother, this type of diabetes must be controlled to protect healthy development of the baby.
The National Institute of Health has found this type of diabetes occurs mostly in around ten percent of the cases. This condition generally resolves itself once pregnancy is over. Having this type of diabetes can, however, place you at a risk for developing non-insulin resistance diabetes at later stages. This can occur within a few years after delivery to as little as a few weeks. Risks to the baby following gestational diabetes include obesity, breathing issues at birth and higher chances of being overweight and diabetic in later life. Mothers may have to undergo C-section due to gestational diabetes which can result in overlarge babies with damage to the heart, nerves, kidney, and eyes. Careful meal planning, gently exercising and regulating weight gain as well as taking insulin to control blood sugar are some of the treatment options for this type of diabetes.
Other Kinds of Diabetes
Rare types of diabetes can result from certain conditions. Diseases of the pancreas, certain types of surgeries and medications or even infections can lead to diabetic symptoms. This is the kind of diabetes that can cause 1 to 5 percent of all kind.
Causes
Photo By: Jessie MNG Lopez/ Wikipedia/ CC BYLack of insulin, production of less insulin or inability of cells in the body to use it effectively leads to either hyperglycemia (high blood sugar levels) or hypoglycemia (low blood glucose levels). The primary problem is type 2 diabetes is that cells of the muscle and fat tissues are affected leading to insulin resistance.
An absolute lack of insulin, generally associated with a destructive process impacting beta cells of the pancreatic organ is the main cause of type 1 diabetes. In type 2 kind, there is a constant fall in beta cells which adds to heightened blood sugar levels.
The Role of Glucose
Glucose, a simple sugar found in food, is an essential nutrient providing enough energy for the proper functioning of bodily cells. Carbs are broken down within the small intestines and its cells then absorb the glucose into the bloodstream. It is then carried as nutrients to the rest of the body by the blood. When insulin lowers, cells become starved of glucose energy because glucose cannot breach cells alone. In specific kinds of diabetes, the cell cannot utilize glucose leading to a lack of nutrition in the midst of plenty.
How Does Insulin Impact the Blood Glucose Levels?
Insulin is a hormone that is the result of specialized beta cells of the pancreas. This is an organ located behind in the stomach. To help glucose access cells, insulin is needed. After eating, blood glucose levels rise. When the levels are lowered, insulin release from the pancreas is in turn decreased. Even in the fasting state, insulin is needed. Lack of insulin or the inability to use this is the reason behind fluctuations in blood glucose levels.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for type 1 diabetes include certain infections and genetic factors.
These are the factors that can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes:
- Obesity
- High BP
- Increased LDL cholesterol and low levels of good cholesterol
- Increased triglycerides in the body
- Inactive lifestyle
- Genetic factors
- Rise in age
- PCOS
- Impaired glucose tolerance
- Resistance to insulin
As far as gestational diabetes is concerned, ethnicity is a major factor. Both genes and environmental factors lead to diabetes.
Obesity
This is the number 1 cause of diabetes. You are more easily capable of developing type 2 diabetes if you have a sedentary lifestyle and suffer from obesity. Extra weight leads to insulin resistance and occurs in people with this type of diabetes. Where the body fat is present also makes a vital difference. More belly fat is linked to insulin resistance and heart diseases and hypertension besides diabetes. Check out your body mass index to see if you are prone to diabetes.
Insulin Resistance
This is a leading cause of diabetes. Muscle, liver, and adipose or fat cells do not use insulin effectively. So, the body produces more initially but over time, enough insulin is not there, and the blood sugar levels go out of control.
Genetic Factors
Both type 1 and 2 diabetes are associated with genetic factors. This disorder is more prevent in certain groups like African American, Latino/Hispanic, Asian American, Alaskan Natives, and American Indians. Genes can also raise the risk of type 2 diabetes by increasing the tendency to become obese.
Gestational Diabetes: Hormonal Factors
Hormones produced in the placenta leading to insulin resistance in pregnant women and causes gestational diabetes. Extra weight, genes and a family history of diabetes have also been associated with gestational diabetes.
Genetic Mutations
Monogenic diabetes is associated with changes or mutated factors in single genes. These pass on from family or happen on their own. The most common types of monogenic diabetes are Type 1 and Type 2. Neonatal diabetes occurs in the first six months of life.
Diseases
Cystic fibrosis causes thick mucus and pancreatic scarring. This in turn prevents the body from producing adequate insulin to meet needs. Another disease, hemochromatosis is associated with storing too much iron, which damages the pancreas and consequently affects insulin production. Some hormonal diseases are also linked to insulin resistance and diabetes.
Cushing’s syndrome is another medical condition where the body produces too much cortisol which is a hormone associated with stress. This affects insulin production. Acromegaly also causes the body to produce too much growth hormone and this leads to insulin resistance. Another hormonal condition associated with diabetes is hyperthyroidism which is when the body produces too much thyroid hormone.
Certain Medications
Specific medications can harm beta cells or the way the insulin works, such as niacin, diuretics, anti-seizure or psychiatric medications, HIC drugs, pentamidine for pneumonia, glucocorticoids for inflammatory diseases and anti-rejection drugs. Statins which reduce bad cholesterol also increase the chances of developing diabetes.
Treatment
Photo By: Bruce Blase/ CC BYLive a long and healthy life by ensuring that you manage your diabetes. Diabetes can affect every part of the body. Manage blood glucose levels through the following ways:
- Follow the diabetic meal plan
- Ensure physical activity is part of your routine
- Check your medicine
- Assess blood glucose levels
- Work with the health care team
The A1C test shows average blood glucose levels and checks if the diabetes is below 7 percent. The goal for those with diabetes is to have a blood pressure count of 140/90mm Hg.
There are two kinds of cholesterol in the blood: HDL or good and LDL or bad. It is the latter cholesterol which clogs the blood vessels and should be cut down on, for diabetic patients.
Quit Smoking
This is another lifestyle change you need to follow. Not smoking is essential because cigarettes make blood vessels in diabetics narrower and make your heart work harder. This also impacts blood sugar levels, cholesterol, BP and blood circulation in a positive way.
Follow a Meal Plan
You need to check with the help from your doctors and medical team. Eat plenty of greens and ensure that you follow a diet that manages your blood glucose, BP and cholesterol levels. Choose natural foods and low-fat products, that are not calorie dense or high in sodium or sugar.
Be Active
Diabetics need to be able to get at least 30 minutes or more of physical activity 4-5 days of the week. Brisk walking is wonderful. Swimming is also a good exercise.
Take Medication
Medicines for diabetes and other health problems is a must even when you have reached BP, blood sugar, and cholesterol goals. Health care professionals should be able to guide you through the process.
Monitor your Conditions
Continuous Glucose monitoring is the right way to check blood sugar levels. This is done by inserting a tiny sensor under the sin which measures the change in blood glucose level. The blood glucose meter can also be used to monitor blood sugar levels. Before the meal, the blood sugar levels should be between 80 to 130 mg/dL. After the meal starts, within two hours, the blood glucose levels should be less than 180 mg/dL.
Diabetics need to check urine for ketones if there are symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis. Ketone levels if too high, can lead to trouble in breathing, nausea, abdominal pain and confusion, This condition is more commonly associated with type 1 diabetes.
Medications
Various kinds of insulin medications are available for people. Short-acting insulin, rapid-acting insulin, regular insulin (Humulin, Novolin), Insulin apart( for example FlexPen) insulin lisper (Humalog) are just some of the common medications. Intermediate-acting insulin includes insulin isophane (Novolin N and Humulin N). Long-acting insulins and insulin Deludec, insulin detemir. insulin glargine and combination insulins may also be recommended.
Amylinomimetic Drugs
Pramlintide or SymlinPen 60/120 is this class of drug. How does it work? You inject this drug before meals which then delays the time the stomach employs to empty itself. Glucagon secretion after meals lowers blood sugar and lowers appetite through a central mechanism.
Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
These are medications that break down sodium and starch, which then lowers blood glucose levels, These include:
- Precose
- Glyset
Biguanides
These medicines lower how much sugar is made by the liver. This decreases how much sugar intestines absorb, making the body more sensitive to insulin. It also enables muscles to absorb glucose. Most common biguanide is metformin. It can be combined with other drugs for type 2 diabetes.
Dopamine Agonist
Called Parlodel, the dopamine-agonist guards against insulin resistance by affecting the rhythms in the body.
DPP-4 Inhibitors
These help the body to make insulin, reducing blood sugar withoutany fluctuations in blood sugar levels, These drugs also help in generating pancreatic insulin. Some of the common DPP-4 inhibitors include:
- Nesina
- Kazano
- Oseni
- Tradjenta
- Glyxambi
- Jentadueto
Glucagon Type Peptides
Incretin mimetic or glucagon-like peptides are drugs which are akin to the natural hormone incretin. This decreases the appetite and how much glucagon is used by the body. These drugs empty the stomach. These include:
- Tanzeum
- Trulicity
- Byetta
- Bydureon
- Victoza
Meglitinides
These are medications that release hormone insulin. In some cases, the drugs may also lower blood sugar levels and include Starlix, Prandin, and Prandimet.
Sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors
SGLT 2 inhibitors prevent the kidneys to hold onto glucose. This helps your body to eliminate glucose easily. Examples of these drugs include Farxiga, Xigduo XR, Invokana, Invokamet) and Jardiance.
Sulfonylureas
These are the oldest class of diabetic medications and they stimulate the pancreas with the aid of beta cells to enable your body to make insulin. These include Amaryl, Duetact, and Avandaryl.
Thiazolidinediones
These are medicines that decrease glucose in the liver and help adipocytes to use insulin better. They, however, are associated with increased heart attack. These drugs include Avandia, Anadaryl, Amaryl M, Actos, Oseni, and Deutact.
Other Drugs
Other drugs which diabetic patients may have to take include aspirin for heart health, statins, high blood pressure drugs like beta blockers.